Managing your finances and understanding your income sources is essential for maintaining financial stability. Two important documents that play a significant role in this process are the paycheck stub and the W-2 form. While both provide information about your earnings, they serve different purposes and contain distinct details. In this article, we will delve into the differences between the paycheck stub and the W-2 form, helping you grasp their unique functions and understand how they contribute to your financial record-keeping.
Paycheck Stub: A Snapshot of Your Earnings
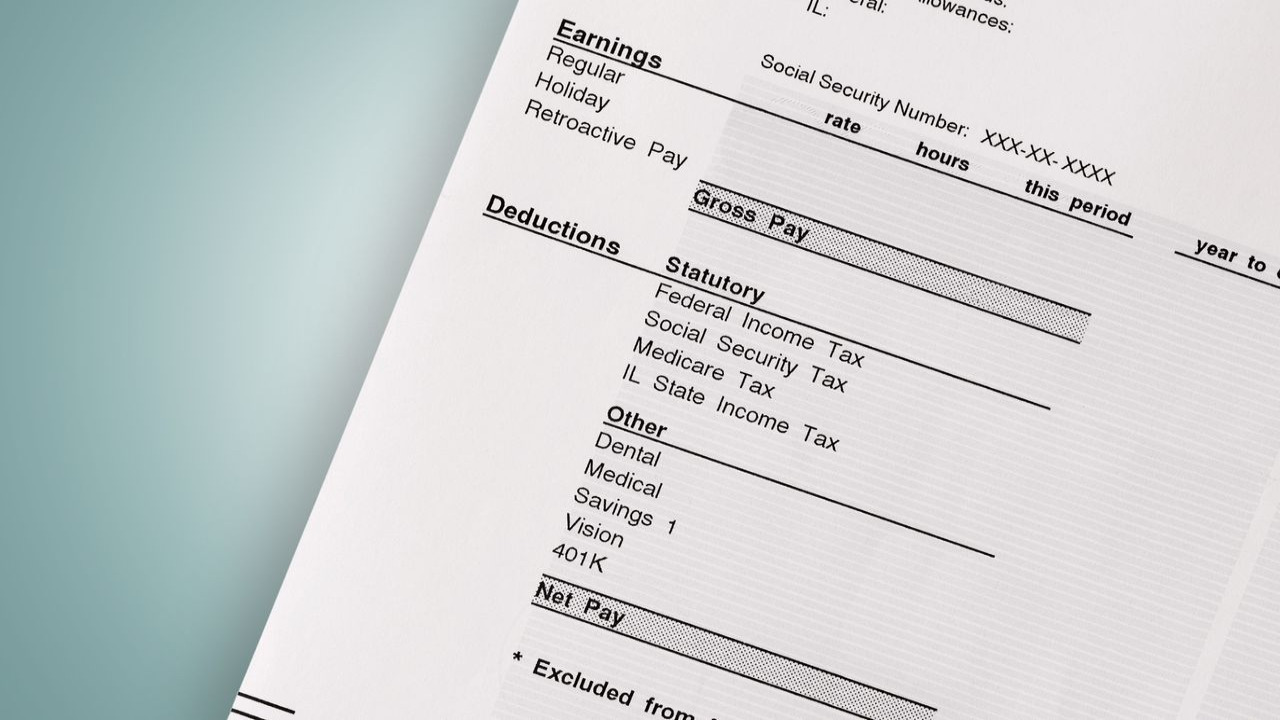
The paycheck stub, also known as a pay stub, is a document provided by your employer that outlines the details of your salary for a specific pay period. There are many helpers for creating paycheck stubs. Create customized pay stubs with PayStubCreator!
Here are some key features of a paycheck stub:
Income Information:
- Gross Earnings: This refers to the total amount of money you earned before any deductions.
- Net Pay: The net pay represents the actual amount you receive after taxes and deductions.
- Taxes: The paycheck stub displays the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck, including federal, state, and local taxes.
- Social Security and Medicare: The stub shows the contributions made towards these government programs.
- Insurance Premiums: If you have health, dental, or any other insurance coverage through your employer, the stub will indicate the amount deducted from your paycheck.
Allowances and Benefits
- Vacation or Sick Time: If you have accrued vacation or sick leave, the stub may include the number of hours available.
- Retirement Contributions: Any contributions you make towards a retirement plan, such as a 401(k), will be listed on the paycheck stub.
- Other Benefits: Some stubs may include additional benefits, such as bonuses or commissions earned during the pay period.
W-2 Form: Summarizing Your Yearly Earnings
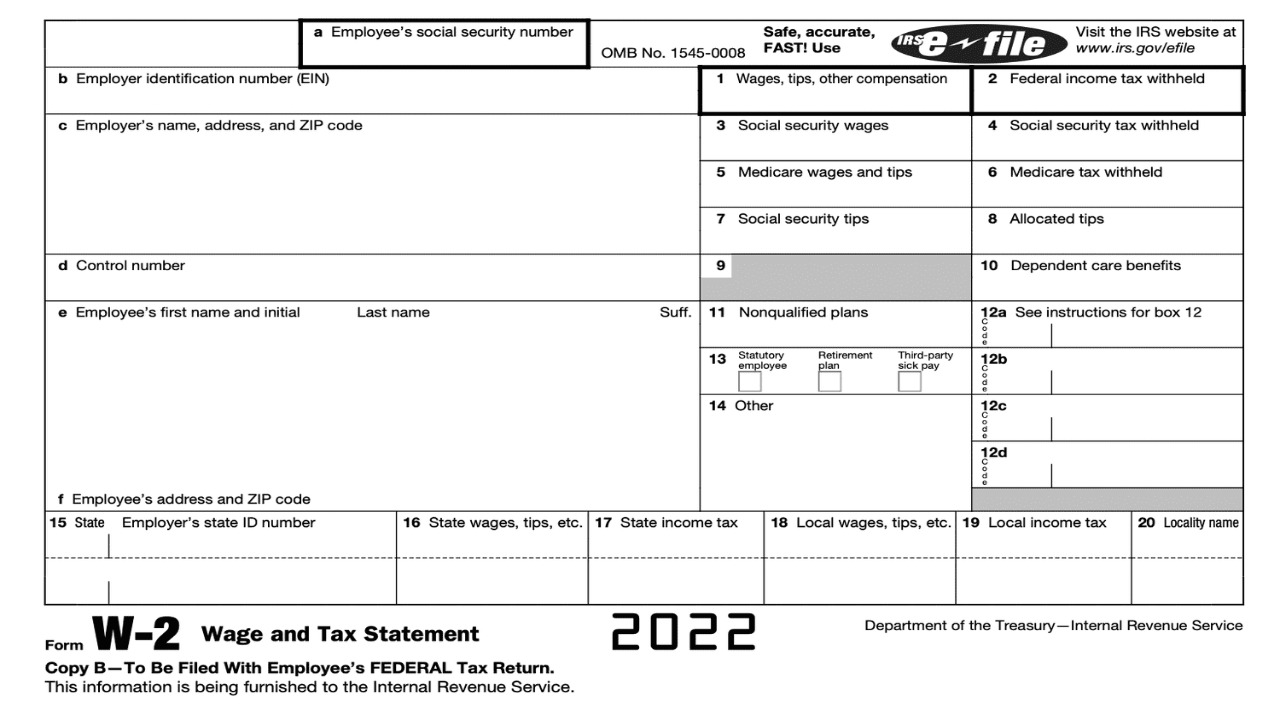
The W-2 form is an important tax document that your employer provides at the end of each calendar year. It encompasses the entire year’s earnings and tax withholdings. Here’s what you need to know about the W-2 form:
Personal Information
- Your Name and Social Security Number: The W-2 form includes your personal identifying information.
- Employer Information: It also contains your employer’s identification details.
- Total Income: The W-2 form reports your total earnings for the year, including salary, tips, bonuses, and other taxable income.
- Tax Withholdings: This section displays the amount of federal, state, and local taxes withheld from your pay throughout the year.
Benefits and Deductions
- Retirement Contributions: Contributions made towards your retirement plan are listed on the W-2 form.
- Health Insurance: If you have employer-provided health insurance, the cost of premiums may be mentioned.
- Other Deductions: The form might include deductions for items like flexible spending accounts or dependent care expenses.
Key Differences and Uses:
Although both the paycheck stub and the W-2 form provide information about your income, they serve different purposes:
Frequency
Paycheck Stub: Issued each time you receive a paycheck, usually on a biweekly or monthly basis.
W-2 Form: Provided annually, summarizing your earnings and tax withholdings for the entire year.
Tax Reporting
Paycheck Stub: Helps you understand your income and deductions but cannot be used for filing your taxes.
W-2 Form: Required for filing your tax return, as it provides the necessary information for reporting your earnings and taxes paid.